Radon Gas Testing in Dallas / Fort Worth and Texas: More Critical For Home Safety Than You Think

Radon Gas Home Inspections in Dallas Texas

20,000 Lung Cancer Deaths Annually in the United States
I had another radon gas inspection job in Garland recently and a remark by one of the interested parties got me to thinking. This was relayed by a third party, but I believe the statement was something along the lines of: “Texas homes do not have a radon problem” which I know to be patently false as I have found homes that tested beyond the EPA action limit of 4 picoCuries/liter including MINE. (I have measured 4.9 – 8.0 pCi/L in the Lake Highlands area which is equal to a pack of cigarettes a day) I have also personally been to several residences that had radon mitigation systems in place, and when they were turned off, the levels went back into the danger zone.
So how do myths and misinformation like this get perpetuated? Radon is a more common issue in other parts of the United States and tends to be more detectable in homes with basements, (as radon is heavier than air) but it is common enough in the North Texas region to be worth checking as a part of indoor air quality testing in Dallas and Fort Worth.
The number of homes in the Dallas, Tarrant, Collin and Denton counties exceed the EPA action limit 5 – 10 % of the time which IS statistically significant; up to 1 out of 10 homes. Furthermore if you add in the number of homes which are marginal (2.0 – 3.9 picoCuries/Liter) as radon gas concentrations vary throughout the day, year, etc. then the number of potentially affected homes in North Texas is closer to 16 – 24 %.
Also, the World Health Organization (WHO) recommends a lower limit than the EPA with the mitigation safety limit set at 2.7 pCi/L versus the higher limit of 4.0 pCi/L by the Environmental Protection Agency. And there is NO SAFE LIMIT of radon gas, any amount is bad, but you can’t get away from it entirely as even outdoor levels are typically 0.3 pCi/L and average indoor is 1.1 – 1.3 pCi/L.
So how dangerous is radon gas? Here is a quick risk comparison by the EPA:
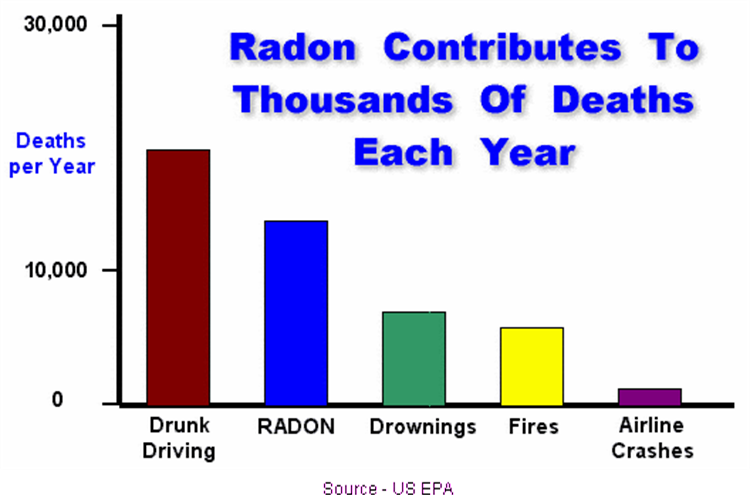
Radon Gas Risk Statistics
This graph shows only 15,000 deaths annually, (the lower number is because the stats are derived from 1986 data quoted by Environmental Science Technology Vol 24 pp. 774 – 1990) but a more recent EPA report (2014) shows closer to an estimated 20,000+ lung cancer deaths annually due to radon – 2nd only to smoking in direct cause – which is actually higher than the fatalities caused by drunk driving in which a great deal of energy has been focused on in recent years.
The problem with radon gas is that it is invisible, silent, and much harder to track than the erratic, weaving driving patterns of an inebriated driver. Couple this with a mythologies like: “Texas homes don’t have radon” or “You need to have a basement for radon to be an issue” and this becomes a significantly overlooked risk and safety factor that is relatively easy to test for and not necessarily that expensive to correct.
How does radon gas do it’s damage? By the emission of inhaled alpha particles that get into the lungs and whose ionizing radiation damages cell DNA. This mechanism works by attacking DNA molecules within the cells to form free radical ions, or changes the molecules themselves into excited molecules that can form biochemical pathways to cancer.
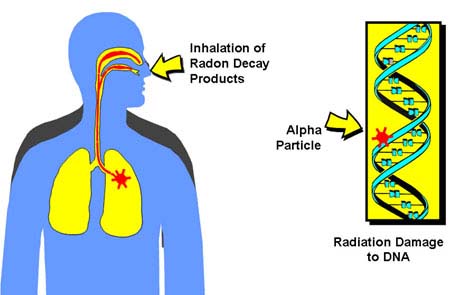
Radon Lung Damage Alpha Radiation
So even if your home has no basement (very few residences in Texas do) then why be concerned? Because the gas can still seep in through cracks in the foundation or gaps in a pier and beam construction. (you don’t need a basement to have a radon issue)
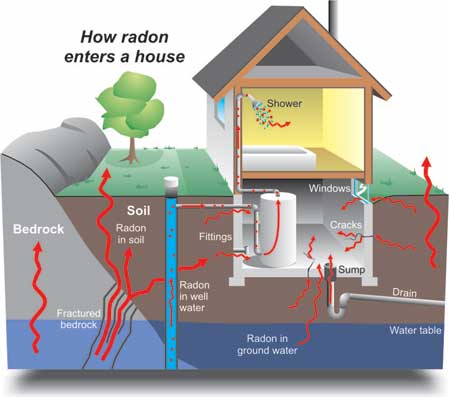
Radon Gas Home Inspection in Dallas / Ft. Worth to find potentially unsafe levels of radioactivity due to these various sources of entry
The solution is to first retest to make sure that the radon levels are consistently high enough to warrant attention and if so, proper ventilation is designed and installed by a professional radon mitigator, and then the residence retested to make sure that the system is working. Incidentally, ScanTech does no mitigation as we consider it a potential conflict of interest.
But for a prospective homeowner who is interested in a property, it is important to get the radon checked as soon as possible once you are inside the option period. The reason why is because of the time delays in deploying the kits, waiting the 48 – 96 hours for the kits to develop, transit time to the lab and the radon lab processing / reporting time. This means a dead minimum of 4 days under IDEAL circumstances with rush fees and hand trucking the kits in to the lab. Otherwise, it can take up to over a week which can easily exceed the standard 10 day option period.
ScanTech does have the ability to check the radon levels with a special digital tester that can get results much more quickly (in as little as 1 – 2 days after deployment) with the same level of accuracy as the activated charcoal radon test kits described above and it is less expensive when comparing a return trip to retrieve the device and interpret the results versus a return trip for the charcoal kits.
The charcoal kit route is more feasible if the testing is not as time sensitive and/or the client is willing to either mail or hand carry the kits into the radon testing lab itself located in Dallas County.
ScanTech has been performing radon testing in the Dallas – Fort Worth area for over 15 years with the procedural expertise and pricing to meet your needs.
We are also AARST-NRPP Certified and able to handle HUD, (LEAN & MAP) GSA, Fannie Mae, Freddie Mac and other multi-family projects including apartments, luxury high rises and senior living / health / memory care facilities.
Radon gas is the 2nd leading cause of lung cancer after smoking and it is a very real problem in the Dallas – Fort Worth area as more than 10 % of all homes have radon levels that are near or exceed the EPA action limit (remediation recommended) of 4 picoCuries/liter and many more exceed the World Health Organization (WHO) recommendation of 2.7 picoCuries/liter.
Q. Where does radon gas come from? Is it everywhere?
A. Radon come from the radioactive decay of radium in the ground which in turn comes from the decay of uranium which can be found in at least trace amounts in ALL soils and rocks, though the amount can vary greatly depending on locale.
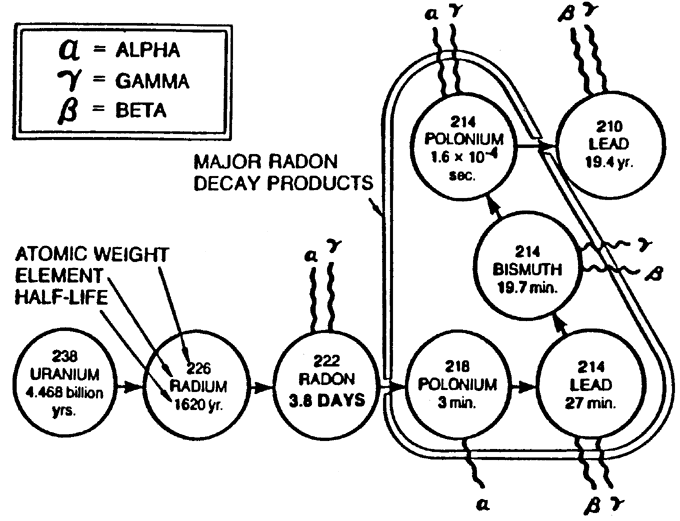
Radon Gas Decay Chart
Q. What factors are important in radon emissions?
A. The largest factor is the geology of the land as emissions are directly dependent on the type of bedrock and deposits involved. Certain granites, shales, phosphatic rocks and minerals containing uranium and radium can potentially release more radon gas, though the pathway efficiency to the surface is influenced by everything from groundwater and CO2 (carbon dioxide) transmission characteristics, to weather and atmospheric conditions such as wind, humidity, rainfall, barometric pressure, as well as soil characteristics and ground topography.
Q. Can radon levels indoors and outdoors be very different from each other?
A. Yes, they can depending on the structure and ventilation of the building. Also, there can be large variances between the outdoor/indoor radon air levels and what you may find in the soil and water.
This is why you generally cannot evaluate the radon levels of a proposed home until after it is built.
More information can be found here:
http://radontestingdallas.com/